If you’ve ever listened to electronic or pop music and noticed a fast series of repeating notes that seem to dance with the beat, you’ve probably heard an arpeggiator in action.
An arpeggiator turns simple chords into rhythmic note patterns automatically. It’s a feature found in many keyboards, synthesizers, and digital audio workstations (DAWs).

Even though it sounds complex, the concept is surprisingly easy to understand. Once you know how arpeggiators work, you’ll see how they shape some of the most familiar sounds in modern music.
Table of Contents:
What is an Arpeggio?
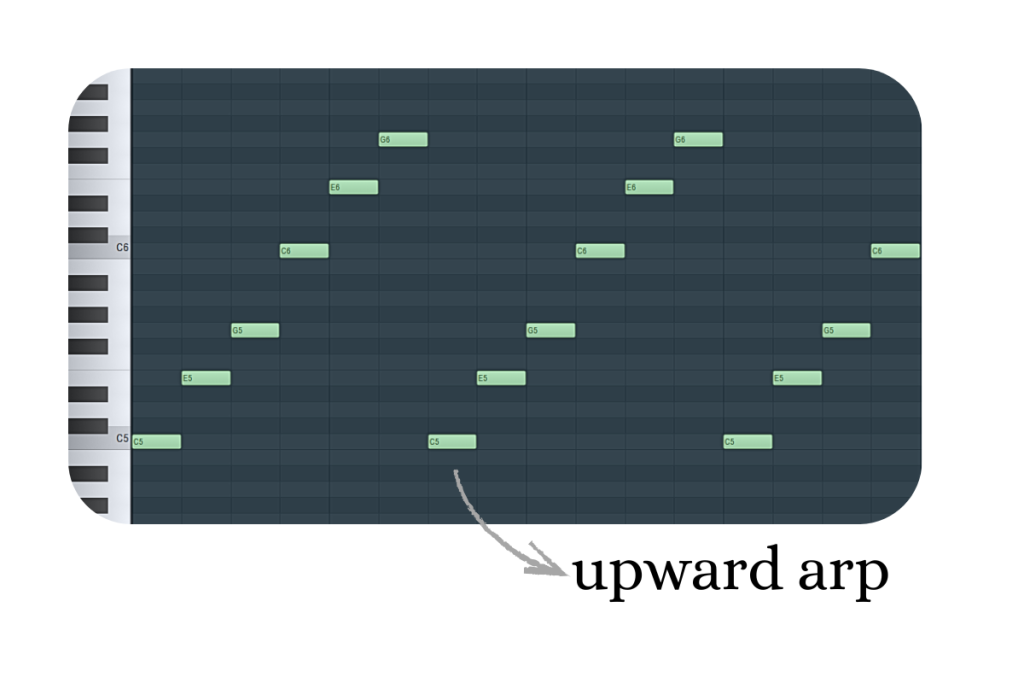
An arpeggio is when you play the notes of a chord one after another, instead of all at once.
For example, a C major chord has three notes: C, E, and G.
If you play them one by one — C, then E, then G — that’s an arpeggio.
Guitarists, pianists, and even vocal arrangers use arpeggios to make melodies smoother and more expressive.
The arpeggio is the musical idea, and the arpeggiator is the machine that performs that idea automatically.
Why Musicians Use Arpeggios?
Musicians use arpeggiators because they make chords sound more dynamic and interesting. Instead of a single sustained sound, you get a moving, rhythmic line that adds energy and depth.
Here are a few common reasons artists rely on them:
- Add movement to simple chords
A flat pad sound can feel dull. Turning it into an arpeggiated pattern instantly gives it rhythm and life.
- Create melodies effortlessly
You can hold down a chord, change the tempo or direction, and the arpeggiator generates melodic ideas for you.
- Fill space in a mix
Arpeggiated notes can sit between the beat and the melody, giving fullness to electronic, pop, or cinematic tracks.
- Stay perfectly in time
Since the arpeggiator syncs to your song’s tempo, it’s always rhythmically correct. No need to worry about timing mistakes.
- Inspire songwriting
Sometimes, turning on an arpeggiator can spark new ideas you wouldn’t have played manually.
Common Arpeggiator Patterns
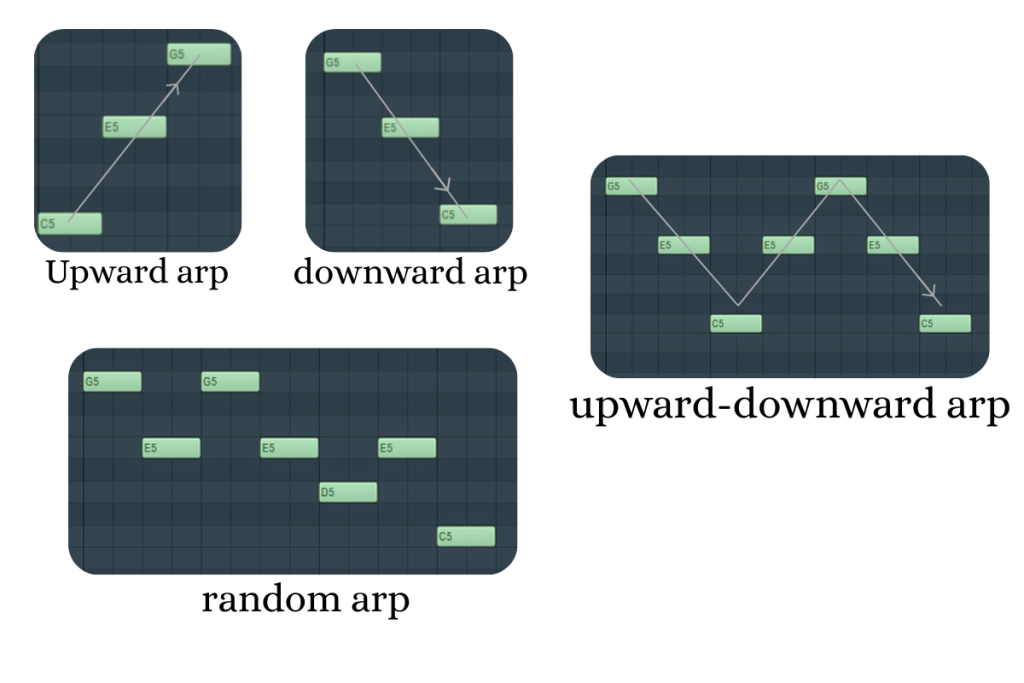
Most arpeggiators let you choose how the notes are arranged. Here are some basic patterns that appear in nearly every synth or DAW:
- Up – plays notes from the lowest to highest (e.g., C–E–G).
- Down – plays notes from the highest to lowest (e.g., G–E–C).
- Up-Down – goes up, then back down (e.g., C–E–G–E–C).
- Random – picks notes randomly from the chord each time.
- As Played – follows the exact order in which you pressed the keys.
You can also control:
- Tempo (how fast it repeats)
- Octave range (how high or low it goes)
- Note length (short or sustained)
Even these small changes can completely transform the feel of a track — from slow, dreamy motion to fast, energetic pulses.
4 Creative Ways to Use Arps
Once you understand the basics, here are some fun and practical ways to use arpeggiators in your music:
1. Build Rhythmic Energy in Electronic Tracks
Set your arpeggiator to a fast tempo and hold a simple chord. Add a soft synth pad underneath for fullness.
This is common in EDM, trance, and synth-pop, where repetitive motion drives the groove.
2. Create Background Motion for Ballads
Use a slower arpeggiator with a gentle piano or plucked sound. It gives emotional songs a subtle rolling feel, similar to finger-picked guitar.
3. Design Basslines Instantly
Instead of programming each bass note, hold one or two keys and let the arpeggiator generate a pulsing rhythm.
Lower octaves make it sound like a moving bass sequence.
4. Inspire Melody Ideas
Sometimes, you don’t know where to start. Turn on an arpeggiator, try different chords, and record the patterns.
You might discover a new hook or melody that becomes the base of your song.
Conclusion
Arpeggiators might sound technical, but they’re one of the easiest ways to make your music sound professional and full of motion.
They take the simple idea of an arpeggio and automate it, freeing you to focus on creativity rather than finger speed.
Whether you’re producing electronic tracks, writing pop songs, or experimenting in your home studio, an arpeggiator can quickly add rhythm, emotion, and energy to your sound.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do arpeggiators do?
An arpeggiator automatically plays the notes of a chord in sequence, creating rhythmic patterns that match your song’s tempo. It turns simple chords into moving, musical lines with different directions and speeds.
What’s the difference between a sequencer and an arpeggiator?
A sequencer plays back pre-recorded notes exactly as programmed.
An arpeggiator generates note patterns live, based on the keys you hold down. The sequencer is fixed; the arpeggiator reacts in real time.
Why is it called arpeggio?
The term comes from the Italian arpeggiare, meaning “to play the harp.”
It describes the flowing way harpists play notes one after another instead of together.
What is the purpose of an arpeggio?
Arpeggios add motion and emotion to chords. They make music sound smoother, more expressive, and rhythmically interesting across all styles.
Are arpeggios difficult to learn?
No. Arpeggios are just chords played note by note. With a little practice, most beginners can learn them easily — or use an arpeggiator to hear how they sound instantly.
