Phase cancellation is an essential term in music mixing. Avoiding it is highly necessary to preserve the quality of the mix. Many beginner producers tend to overlook this, which ultimately results in a loss of frequencies and, consequently, poor mix quality.

In this blog, you will learn everything about phase cancellation, from the outcomes of this issue to ways to fix it. Additionally, methods for detecting this notable issue will be discussed.
Definition of Phase cancellation

Phase cancellation occurs when two sounds with similar frequencies are out of sync. Instead of sounding fuller, the misaligned waveforms cancel each other out. This results in a thinner, hollow, or even silent sound due to the loss of specific frequencies. Phase cancellation is a common issue in multi-mic recordings or when layering sounds, which can negatively impact the clarity and balance of your mix.
For example, when two guitar sounds are played together, the strumming might sound weak due to phase cancellation. Another example is when two microphones capture the same sound, but with a slight time difference, phase issues can arise.
Why should we care about phase cancellation?
When two similar audio signals are out of phase, specific frequencies disappear. This compromises the overall quality of your entire mix, resulting in a muddy sound.
Mono-compatibility
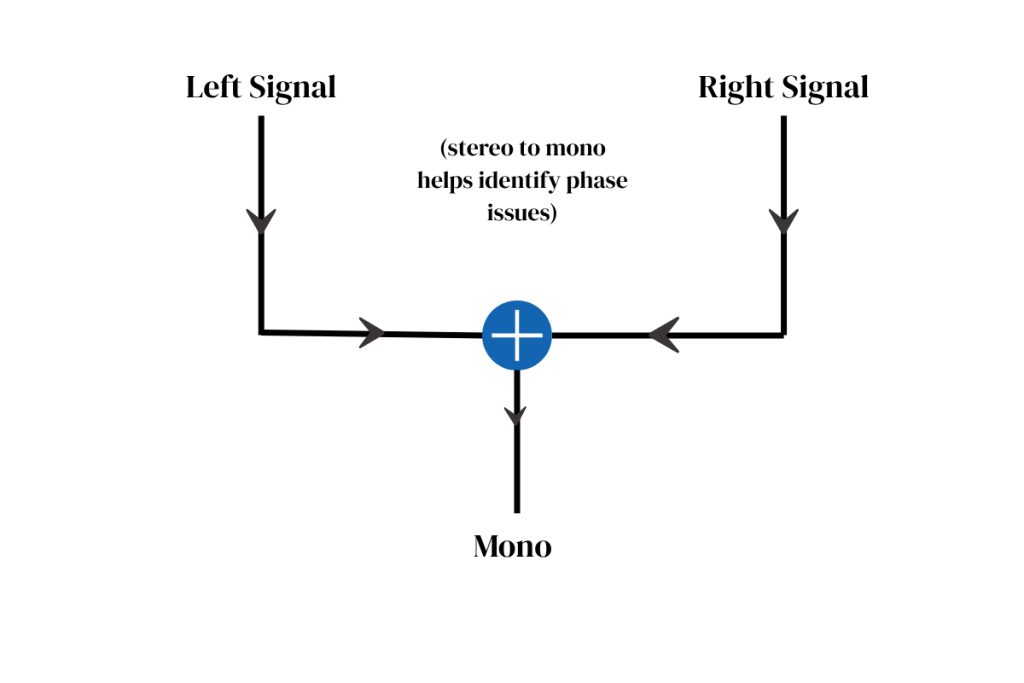
One of the biggest concerns is mono compatibility. Many playback systems (like phones or Bluetooth speakers) play audio in mono. If your mix has phase issues, sounds that work fine in stereo might disappear or sound weak in mono. This can harm your listener’s experience and the impact of your music.
Muddy mix
When instruments or vocals clash due to phase problems, it becomes hard to distinguish each element. You might boost EQs or compress more in an attempt to fix it, but the real issue lies in the phase alignment.
Hollow Sound
Out-of-phase signals often cancel critical frequencies, especially in the low end. This results in a hollow or thin sound, where your mix lacks warmth and depth. Even if all instruments are present, the overall result feels empty or weak.
Difficulty in Mixing
Phase issues confuse the mixing process. Things don’t sit well in the mix, levels seem off, and effects don’t behave as expected. You may spend hours trying to fix problems that are caused by poor audio phase alignment.
Even well-recorded instruments can suffer if the microphones are not positioned correctly or if layers are not properly time-aligned. That’s why understanding the phase in audio is highly essential.
How do you recognise phase issues?
Detecting phase issues in a mix is relatively easy. There are specific ways to identify these issues.
Listen to your mix carefully by turning it to mono.
When your mix is turned to mono, you suddenly feel that it lacks energy. Vocals are suppressed; kicks and snares don’t have that same punch. This lack of energy can mainly be because of phase cancellation.
The correlation meter helps in detecting phase issues

A correlation meter is essentially a tool used to detect phase issues that may be present in your mix. These tools have a visual representation that can easily simplify the process. There are many tools to choose from, such as Voxengo Correlometer, ADPTR Metric AB, and Flux Stereo Tool, among others.
Flip the phase

Flipping the phase simply means reversing the direction of the sound wave. Turning its peaks into dips and dips into peaks. Many mixers or plugins have a phase (Ø) button that does this instantly. If you flip the phase on one track and the mix suddenly sounds fuller or clearer, it means those tracks were canceling each other out. This simple trick helps reveal and fix phase cancellation quickly during mixing.
Ways to Avoid Phase Cancellation
Here are some simple yet effective ways to avoid phase issues in your mix.
Microphone placement: 3:1 rule
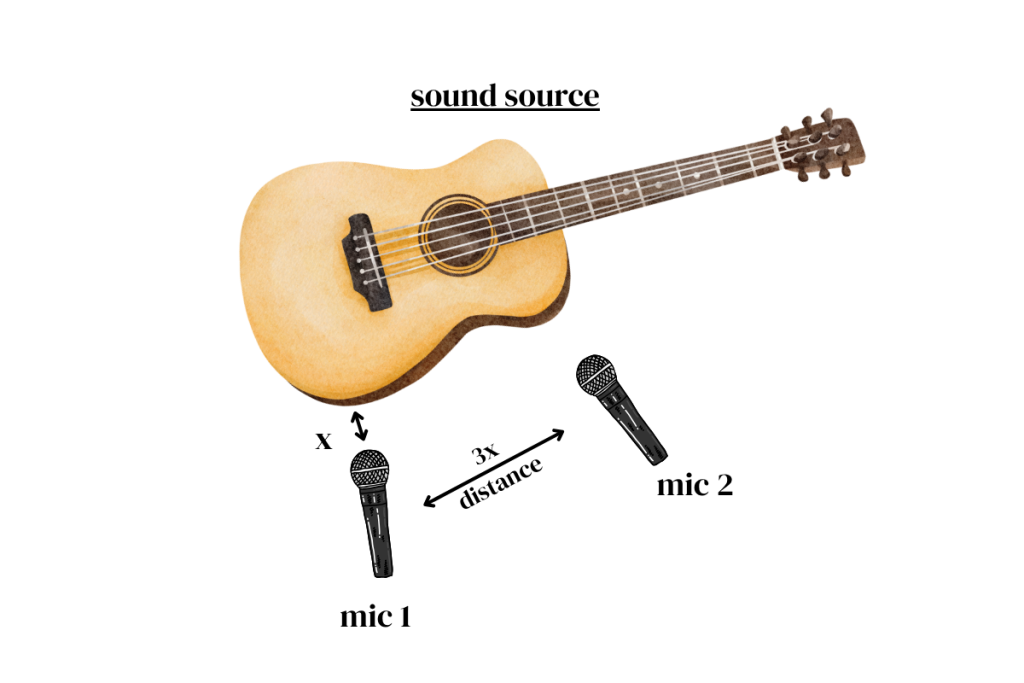

When recording with multiple microphones, follow the 3:1 rule: place the second mic at least three times farther from the source than the first. This helps reduce phase differences caused by sound arriving at slightly different times.
Check for phase while double-tracking
Double tracking is the process of recording a sound twice and combining the two recordings to create a fuller and wider sound. However, while doing this, phase issues can arise. Misaligned waveforms can cancel each other out. Zoom in and manually adjust if needed.
Check your mix in mono.
Always test your mix in mono. This helps reveal phase issues that might be hidden in stereo playback. If something sounds hollow, quieter, or muddy in mono, it’s a red flag.
Be Careful with Time-Based Effects
Delays, choruses, and reverbs can alter timing and introduce phase issues if not used carefully. Try to keep the effects balanced between the left and right channels, and check their impact in mono.
Avoid Overcrowding the Same Frequency Range
Try to keep your mix simple and not overcrowd frequencies. Doing this can avoid frequencies from getting cancelled out. Use EQ to carve out space and therefore, avoid overlapping energy.
FAQ
What can cause phase issues in audio?
Using multiple microphones, duplicating tracks without alignment, or poorly layered effects like delay and reverb can cause phase issues.
How to deal with phase cancellation?
Check your mix in mono, flip the phase on suspicious tracks, align the waveforms manually, and use phase correction plugins if necessary.
Do phase issues ruin my mix?
Yes, they can. Phase problems can make your mix sound thin, muddy, or cause key elements to disappear, especially in mono playback.
Is phase cancellation good?
Usually no, but in some cases, creative use of phase can add stereo width or unique textures, only if done intentionally and carefully.
Conclusion
Phase cancellation can seriously affect your mix. It can make your audio sound weak, muddy, or hollow. Sometimes, parts of your track might even disappear in mono. But it’s easy to avoid with a few simple steps. Listen in mono. Align your tracks. Use phase flip tools if needed. Fixing phase issues makes your mix clearer and more balanced. Understanding phase in audio helps your music sound better on every speaker, from phones to pro systems.
